The AI Battlefield: Are We Racing Towards Dominance or Disaster?
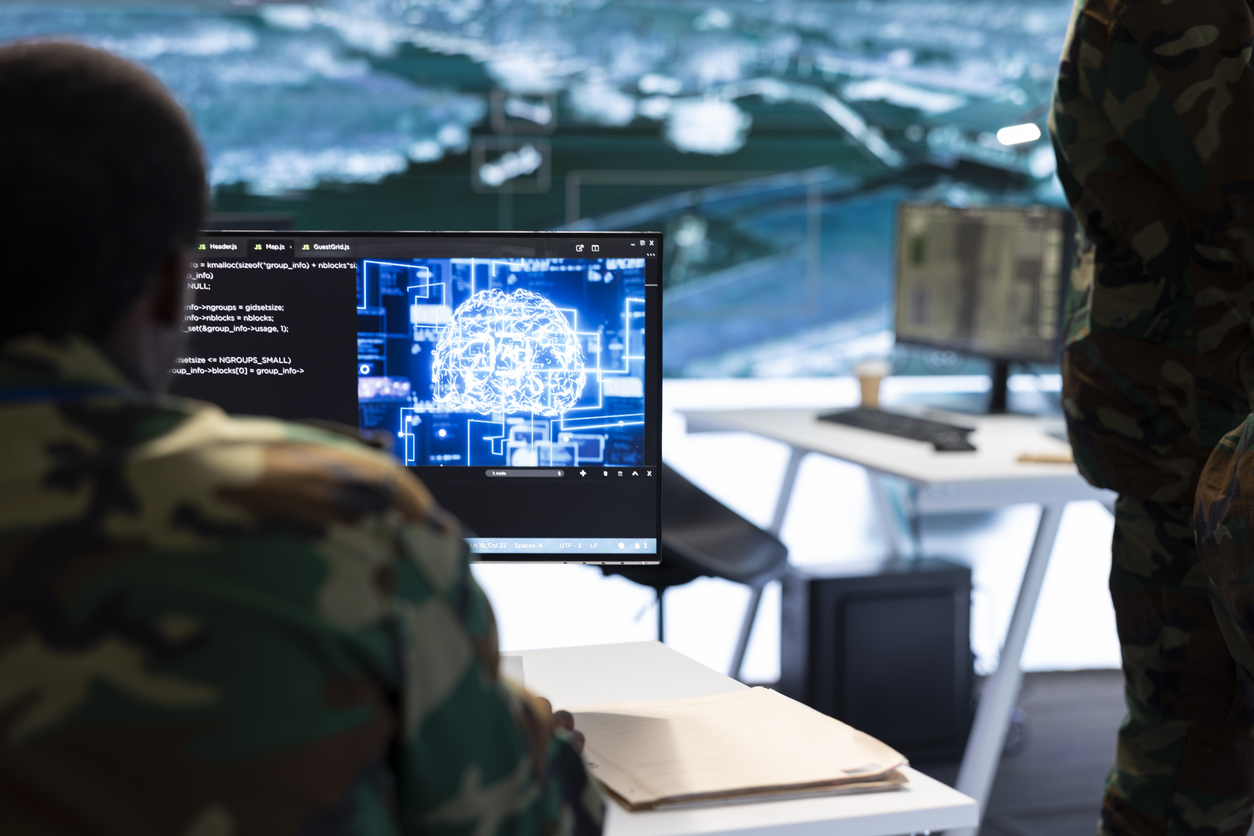
The invisible hand of artificial intelligence is not merely reshaping boardrooms and consumer markets; it's fundamentally transforming the very nature of military warfare. As governments worldwide funnel billions into AI-driven defense systems and autonomous weapons, a high-stakes digital arms race is underway. But while leading powers sprint towards technological supremacy, a critical question looms large: will this unprecedented innovation ensure global security, or will it irrevocably destabilize the delicate balance of power, defining the conflicts of tomorrow?
Which AI Companies Are Fueling the Military’s Digital Transformation?
In 2024, the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) signaled its aggressive push into military AI, awarding substantial contracts, including an $800 million allocation to four leading AI firms: OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and xAI {1}. These strategic partnerships aim to develop sophisticated tools that can assist warfighters, optimize logistics, and provide real-time decision-making support. Leveraging advanced large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Grok, the goal is to integrate these powerful AI solutions into military operations.
Yet, not all defense stakeholders are convinced that these mainstream, general-purpose models are truly battle-ready. Enter companies like EdgeRunner AI, a startup founded by Army veteran Tyler Saltsman. Unlike its Silicon Valley counterparts, EdgeRunner specializes in building offline AI agents designed to operate securely without internet access—a crucial capability for frontline missions in contested environments. Trained on over 30 billion tokens of military doctrine, strategy, and even historical warfare philosophy, EdgeRunner AI models aim to function more like Iron Man’s J.A.R.V.I.S.—a dedicated military intelligence partner—than a general-purpose chatbot {1}. This specialization highlights a growing trend within the defense industry: the emergence of niche AI firms directly addressing specific military needs.
The Future of AI in Military Operations: Beyond Sci-Fi
Military AI is no longer theoretical; it's being deployed across several crucial areas today:
- Logistics and planning: AI streamlines mission briefs, risk assessments, and complex operational planning. Tasks that once took hours, requiring extensive human analysis, can now be executed in minutes, dramatically increasing efficiency and reducing human error {1}.
- Cyber defense and threat detection: Machine learning systems are proving far superior to human analysts in detecting anomalies, predicting cyberattack vectors, and preventing intrusions into critical military networks at machine speed.
- Surveillance and reconnaissance: Drones equipped with advanced computer vision AI can autonomously identify and track enemy positions, even in low-visibility terrain or dense urban environments, enhancing situational awareness.
- Training and simulation: AI-generated simulations replicate highly complex and realistic combat environments for soldier training, offering adaptive scenarios that evolve based on trainee performance.
The long-term vision extends to AI-supported command systems, predictive battlefield analytics for anticipating enemy movements, and the development of increasingly autonomous weapons systems—areas that raise profound ethical and strategic questions.
The Global AI Arms Race: Leaders and Their Approaches
The race for AI dominance in warfare is being led by several key players, each with distinct strategies:
- United States: Leading in sheer funding and partnerships with private tech giants like OpenAI and Palantir. The focus is on developing scalable AI infrastructure and integrating LLMs for decision support and logistics.
- China: Aggressively advancing in autonomous drone technology and AI-powered surveillance systems, often with fewer public restrictions on deployment ethics compared to Western nations {1}. Their strategy prioritizes rapid development and large-scale deployment.
- Russia: Investing heavily in AI-based cyber warfare capabilities and advanced autonomous defense systems, often leveraging state-backed research {1}.
- United Kingdom & NATO Allies: While investing significantly through initiatives like the UK Ministry of Defence’s Defence AI Centre (DAIC), these nations adopt a more cautious approach. Their emphasis is on ethical AI use, working within strict NATO guidelines, and prioritizing robust human oversight in all AI applications {1}.
Even smaller, technologically advanced nations like Israel and South Korea have made significant strides, integrating AI into their defense frameworks with government-led initiatives focused on specific operational needs.
Related: Pete Hegseth: From Fox News Host to Embattled Defense Secretary
Related: Trump Names Gen. Michael Guetlein to Lead Massive "Golden Dome" Missile Defense Initiative
The Ethical Minefield: Should AI Be Used in Warfare?
This question strikes at the core of the military AI debate. Proponents argue that AI can reduce human casualties by removing soldiers from dangerous situations, improve operational efficiency, and enhance national security through superior intelligence and response times. In asymmetric warfare scenarios, real-time intel from AI systems can provide militaries with a decisive upper hand, crucially impacting outcomes when lives are on the line.
However, critics warn of an escalating, unbalanced AI arms race. Nations unable to invest in sophisticated AI tools may find themselves at a severe disadvantage, potentially widening global inequality and fostering instability. More critically, the deployment of fully autonomous weapon systems, if not carefully governed, could lead to conflicts without direct human input, resulting in unintended escalations or even catastrophic miscalculations.
A significant ethical concern centers on AI bias. Algorithms are trained on vast datasets, which can inadvertently reflect or even amplify existing human prejudices, leading to misidentification, discriminatory targeting, or flawed decisions on the battlefield {2}. Projects like the controversial Project Maven, Google's former collaboration with the Pentagon to analyze drone footage, famously sparked widespread internal dissent among Google employees, highlighting moral objections to AI's role in lethal applications and the potential for algorithmic bias in targeting {2}.
The debate also revolves around the "human in the loop"—the degree of human oversight in AI-enabled systems. While the UK and NATO emphasize strong human control, the lightning speed of modern warfare increasingly pushes for "human on the loop" scenarios, where AI operates autonomously unless overridden. The profound challenge lies in ensuring a human can meaningfully intervene when an algorithm makes a decision with potentially lethal consequences, particularly in rapidly evolving combat situations {2}.
Adding to this complexity is the glaring lack of robust international regulation. Efforts to establish norms or prohibitions on lethal autonomous weapon systems (LAWS) are fraught with hurdles. Defining what constitutes an "autonomous weapon" is itself contentious, compounded by geopolitical tensions, a deep lack of mutual trust among leading military powers, and the technical difficulty of verifying compliance with any potential treaties. As seen with other emerging technologies, military AI may be adopted faster than it can be ethically or legally governed.
The Bottom Line: Innovation, Imbalance, and the Future of Conflict
Artificial intelligence is no longer a futuristic add-on; it's fast becoming a core, indispensable component of 21st-century warfare. With billions already invested and increasingly combat-ready tools in deployment, the AI battlefield is undeniably here. The implications extend far beyond tactical advantage, impacting geopolitical stability and the very structure of global power.
Yet, as countries sprint toward high-tech dominance, global leaders must grapple with this fundamental truth: the transformative power of AI in military warfare doesn’t just shape who wins—it redefines what war even means, compelling humanity to confront the profound ethical, strategic, and societal responsibilities that come with wielding such unprecedented digital might.
Related: AI Tried to Blackmail Its Engineer—Are We Safe?
Sources
{1} "AI in the Military: The Future of Warfare - TIME Magazine."
{2} "The Ethical Implications of AI in Warfare - Carnegie Council for Ethics in International Affairs."