Denise Coates 2025 Pay: How Britain’s Richest Woman Earned Over £280m While Company Profits Fell
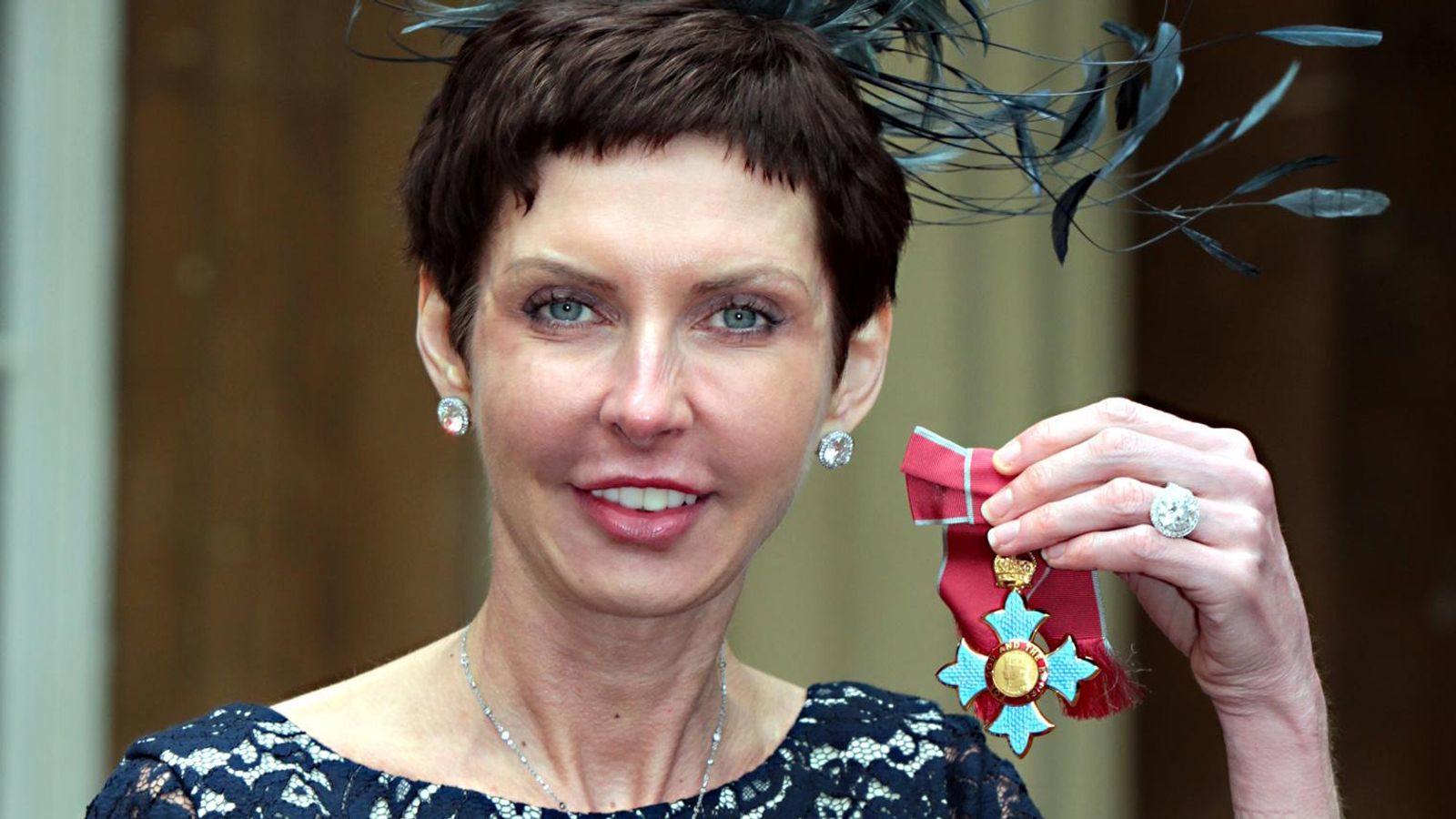
Denise Coates, the billionaire founder of Bet365, took home over £280m in salary and dividends in 2025, according to published accounts — nearly double the largest FTSE 100 CEO payout and around 60 times the average UK worker’s annual salary.
This record sum comes even as Bet365’s pre-tax profits fell from £627m to £349m, highlighting a stark contrast between founder wealth and company performance.
Her payout isn’t just a headline figure; it’s a vivid example of how founder control and ownership leverage can shield personal earnings, even when operational costs rise, expansion is expensive, and markets are exited. For the public and business-interested readers alike, the story underscores how billionaire founders maintain cash flow and financial authority, while the broader company absorbs costs and friction.
Founder Pay Protected Despite £325m Cost Surge
In 2025, Coates drew £104m in salary and was entitled to at least half of a £353.6m dividend. Meanwhile, Bet365 incurred £325m in additional expenses tied to licensing, staffing, technology, and market exits, according to public filings.
This creates a tangible tension: while executive pay remains protected, operational budgets feel the pressure. Teams managing day-to-day operations face constrained resources, delayed approvals, and more complex vendor negotiations. Across industries, this dynamic highlights the influence of founder ownership and the uneven distribution of financial risk within a company.
How Expansion Into the US and South America Stretches Company Budgets
Bet365 expanded into five new US states and additional South American markets in 2025, requiring substantial investment in compliance, infrastructure, and staffing. While the company absorbs these costs, Coates’s personal pay remains unaffected.
This imbalance demonstrates a practical lesson for any business: rapid growth and regulatory compliance often create friction for operational teams, while owners with concentrated control maintain financial flexibility. Recognizing this dynamic helps teams anticipate budget limitations, plan resources efficiently, and understand how leverage shapes company decisions.
Why Regulatory Exits Leave Founder Earnings Untouched
The company’s withdrawal from China and other high-risk regions cost £59m in one-off restructuring expenses (public filings, 2025). While these costs impact internal budgets and operational planning, Coates’s dividend and salary remain untouched.
This illustrates a wider commercial consequence: founders with majority ownership can shield themselves from market or regulatory risks, leaving the operational burden on employees and the company. Any business with concentrated ownership will see similar dynamics, emphasizing the importance of understanding where leverage and responsibility truly lie.
Dividend Control: How Coates Keeps Cash Flow in Her Hands
Majority ownership allows Coates to control the timing and size of dividend payments, ensuring executive earnings continue even when company profits fluctuate.
For the company, this creates subtle but important friction: day-to-day budgets, project approvals, and vendor payments may be constrained while executive payouts remain intact. Understanding dividend authority and founder leverage is crucial for predicting operational bottlenecks and planning effective resource allocation.
Executive Takeaway
Denise Coates’s 2025 earnings show a universal principle: founder ownership can protect personal pay even when company profits fall and operational costs rise. Operational teams absorb budgetary pressures and friction, while the founder maintains control over cash flow and dividends. Recognizing these dynamics is key for anyone interested in how founder-led businesses manage wealth, risk, and operational execution.
FAQs
Q: How much did Denise Coates earn in 2025?
A: Over £280m in salary and dividends, reflecting her majority ownership stake.
Q: Why is her pay unaffected by falling profits?
A: Majority ownership allows her dividend and salary rights to continue independent of company performance.
Q: How do expansion costs affect company operations?
A: Operational teams absorb licensing, compliance, infrastructure, and staffing costs, creating budget pressure and delays.
Q: Who benefits most from founder pay insulation?
A: The founder, who retains control over cash flow and dividend timing.
Q: Who bears the operational friction?
A: Employees, finance teams, and vendors experience tighter budgets, slower approvals, and increased negotiation challenges.
Q: Is this dynamic unique to gambling companies?
A: No. Any founder-led or majority-owned company can experience similar pay versus operational tension.
Q: How do regulatory exits affect internal budgets?
A: Costs from restructuring and compliance fall on the company, while founder payouts remain intact.
Q: Why is this situation evergreen?
A: Founder pay insulation and operational friction recur in any business where ownership is concentrated.
Q: How does this story relate to public interest?
A: The contrast between founder pay and company costs highlights wealth, authority, and control, attracting wide readership.
Q: What lessons can other businesses learn?
A: Recognizing owner leverage and cash allocation authority helps anticipate budget friction, vendor pressures, and execution challenges.
Latest: 🟡 Nvidia to Poach Groq Staff: The AI Talent War That Will Rewrite Hiring Budgets