Xiaomi Declares War on Tesla, Apple & Huawei in Tech Shakeup
From budget smartphones to electric supercars and cutting-edge chips, Xiaomi is rewriting what it means to be a Chinese tech company.
In a bold livestreamed event from Beijing, Xiaomi CEO and founder Lei Jun unveiled the company’s most ambitious innovations yet: a high-performance electric SUV called the YU7, and a self-designed 3-nanometer smartphone chip—the Xring O1. This move, aimed squarely at titans like Tesla, Apple, and Huawei, marks a dramatic transformation from Xiaomi’s origins in low-cost consumer electronics.
Who Owns Xiaomi?
Xiaomi Corporation is a publicly traded company listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX: 1810). While no single individual "owns" Xiaomi outright, its largest shareholder and public face is Lei Jun, the billionaire entrepreneur who co-founded the company in 2010. Lei is both CEO and Chairman, and remains the driving visionary behind Xiaomi’s expansion into electric vehicles (EVs), semiconductors, and smart hardware ecosystems.

Lei Jun
Are Xiaomi and Huawei the Same Company?
No—Xiaomi and Huawei are two separate, competing tech giants based in China.
-
Huawei: Founded in 1987, Huawei focuses on telecom infrastructure, smartphones, and enterprise solutions. It has faced heavy U.S. sanctions limiting its access to advanced chips and foreign markets.
-
Xiaomi: Founded in 2010, Xiaomi started with smartphones and quickly became known for high-spec devices at budget prices. It has since expanded into TVs, smart home gadgets, wearables—and now, electric vehicles and semiconductor design.
While both companies are part of Beijing’s push for technological self-reliance, they are rivals, particularly in smartphones and now, chip development.
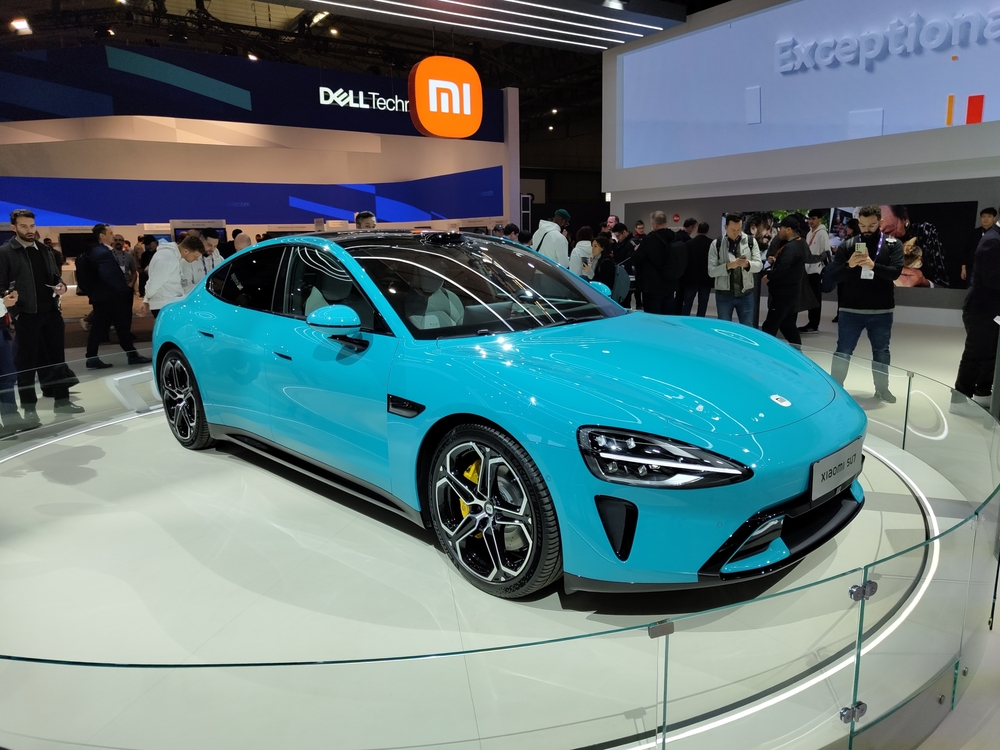

Xiaomi’s Bold Expansion into EVs
The star of the show was the YU7 SUV, Xiaomi’s first electric SUV, designed to take on Tesla’s Model Y and Porsche’s Macan EV. Highlights include:
-
835 km (518 miles) range on a single charge
-
0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) in just over 3 seconds
-
Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
-
Scheduled market release: July 2025
-
No pricing or pre-order timeline yet
This follows Xiaomi’s first EV, the SU7 sedan, which faced criticism after a fatal crash in March sparked safety concerns and order cancellations.
Related: Ford’s CEO Praises Xiaomi’s SU7
Xiaomi Enters the Chip War
Even more significant was the launch of the Xring O1 chip, a 3-nanometer processor designed in-house to power Xiaomi’s flagship smartphones and tablets. It’s a direct answer to Apple’s A18 Pro and Qualcomm’s Snapdragon elite chips.
Key claims from Lei Jun:
-
Outperforms the Apple A18 Pro in thermal efficiency during gaming
-
Debuts in the Xiaomi 15S Pro smartphone (¥5,499 or ~$764)
-
Manufactured by TSMC, the world’s leading chip foundry
-
Represents a ¥13.5 billion ($1.87 billion) investment in R&D
-
Future roadmap includes ¥50 billion ($7B) in chip R&D over the next decade
This achievement also puts Xiaomi ahead of Huawei, which currently struggles to make chips smaller than 7nm due to U.S. sanctions and its inability to work with TSMC.
A Broader Geopolitical and Tech Strategy
Xiaomi’s diversification into autos and chips is not just corporate strategy—it’s geopolitical maneuvering.
-
China wants to end its reliance on U.S. tech, and Xiaomi is becoming a key player in that vision.
-
Beijing’s state media praised the chip as a national “breakthrough,” showcasing the ability of private firms to lead innovation in a hostile global climate.
-
Xiaomi’s rise comes amid a broader U.S.-China tech rivalry, particularly over AI chips and semiconductor access.
Related: Robots Race Humans in Historic Beijing Half-Marathon
Conclusion
With its eyes set on Tesla’s roads, Apple’s chips, and Huawei’s home turf, Xiaomi is evolving from a budget phone brand to a tech juggernaut shaping the future of mobility, computing, and consumer electronics.
The question isn’t whether Xiaomi can compete with Silicon Valley—it’s how soon before Silicon Valley starts watching Xiaomi’s every move.